What is Peripheral Neuropathy?
Did you know?
The term comes from a combination of two words: NEURO which means “nerves” and PATHY which means “disorder”, so it is a disorder of the nerves.
When the nerves affected are those beyond the brain and the spinal cord, the condition is called “peripheral neuropathy”.
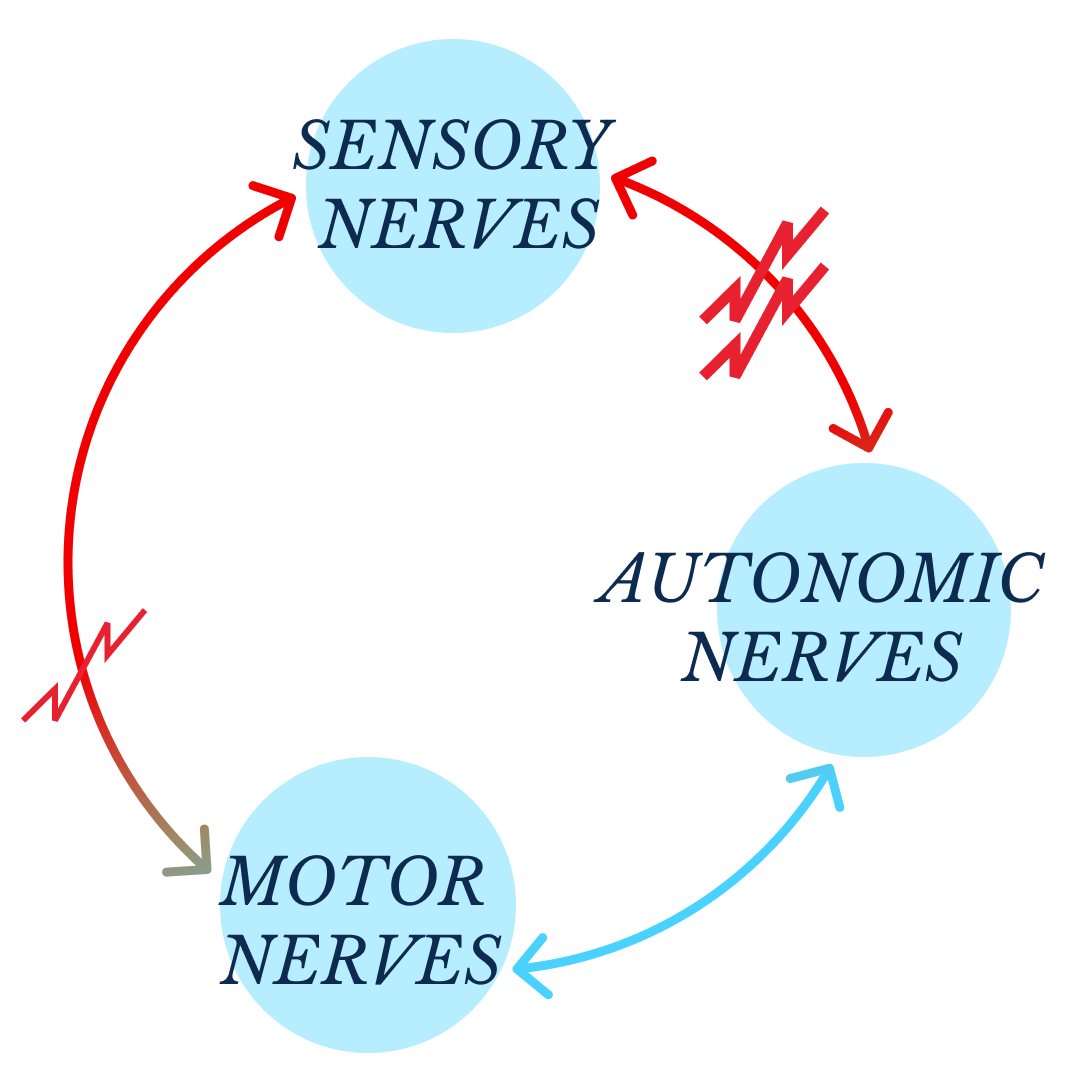
You could either have a dysregulation of the sensory fibers, the motor fibers, the autonomic or all of them at once.
- Sensory nerves: receive sensation, such as temperature, pain, vibration or touch, from the skin
- Motor nerves: control muscle movement
- Autonomic nerves: control functions such as blood pressure, perspiration, heart rate, digestion and bladder function
What are the basic concepts of our nervous system?
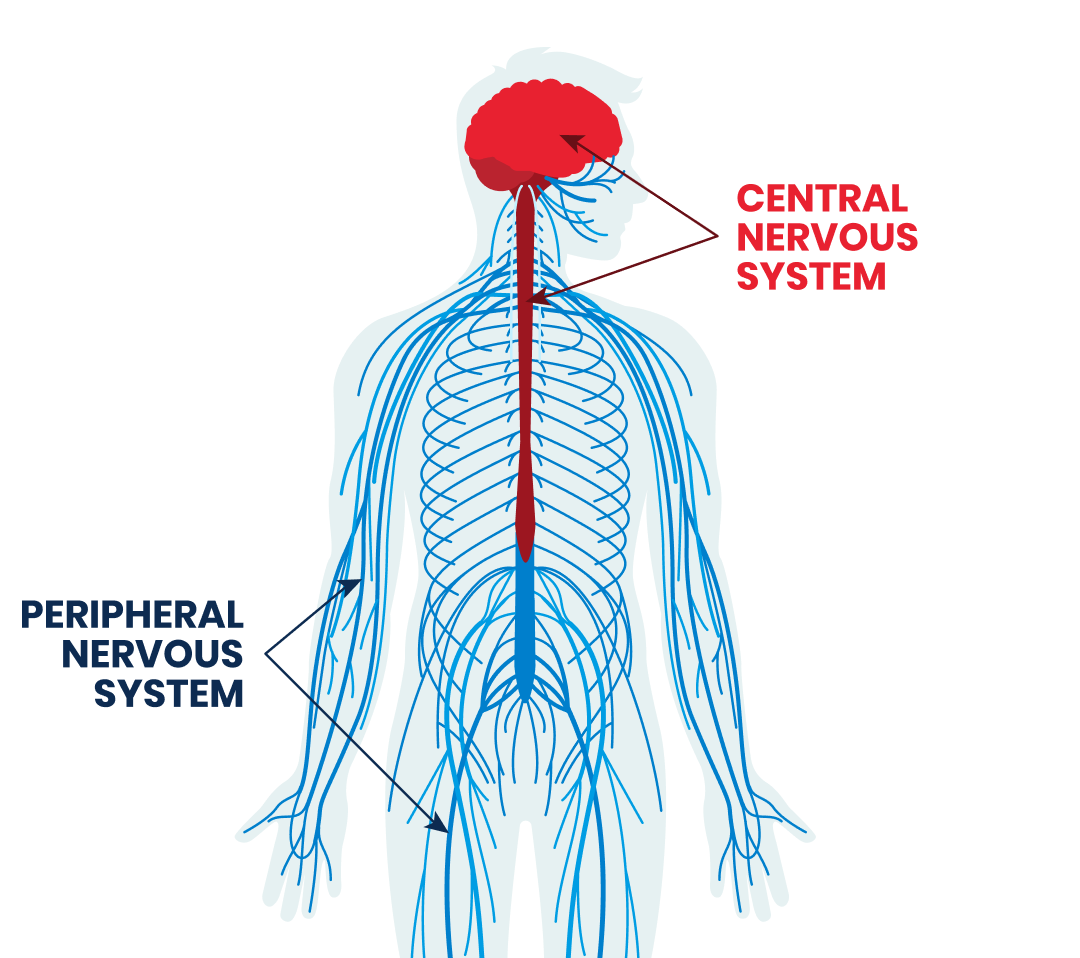
Our nervous system is the one in charge of receiving and transmitting all signaling and messages throughout our body. It is formed by two parts, the CENTRAL Nervous System (brain and spinal cord) and the PERIPHERAL nervous system (nerve branches).
The brain and the spinal cord are in the head and inside the spinal canal respectively. In other hand, the peripheral nervous system refers to all the parts of the nerves outside the brain and the spinal cord, it includes all the nerves, roots and branches spread out in your body, think about the PNS as the “wire system” in any electronic machine. So, the brain is the command center that receives interprets and transmit all messages using the Peripheral nervous system as the transmitter.
These nerve branches are composed of 3 different fibers or types: motor, sensory and autonomic, each one of these helps you move, feel all sensations throughout your body, sensations such as touch, changes in temperature (cold or hot), vibration, pressure, and pain in all and regulates body temperature and sweat.
What are the symptoms of peripheral neuropathy ?
Common symptoms of peripheral neuropathy include sensory origin such as burning, shooting, electric shock type sensations, pins and needles, numbness and tingling sensation that comes and goes.
The dysregulation could be so severe that sometimes these nerve branches are damage to the point that even a normal touch could be felt as pain, condition called Allodynia, or in other instances a minor pain stimulus for example a gentle pressure with a toothpick may be felt as a severe shooting pain similar of what you could have felt if you cut yourself with a knife, condition called Hyperalgesia, basically is an exaggerated pain response.
Other presentations include loss of sensation, loss of balance and coordination, muscle weakness or paralysis if the motor fibers are affected and if the autonomic fibers are affected you will notice trouble with excessive sweating, digestive issues, low blood pressure, with associated dizziness and lightheaded just to mention a few.
Sometimes minor pain stimulus may be felt as a severe shooting pain similar of what you could have felt if you cut yourself with a knife.
What causes peripheral neuropathy?
Peripheral Neuropathy may be cause by many different conditions, and sometimes you may have not only one but multiple causes, reason why it is so difficult to control.
→ Traumatic injuries or repetitive stress
A job or a hobby that put continuous stress over the nerves for long periods of time, can cause nerve irritation, inflammation and subsequent nerve damage. For example, certain sports such as golf, tennis or playing certain instruments such as violin, viola put your nerves at risk of chronic inflammation, carpal tunnel is another good example of chronic nerve trauma.
→ Infectious conditions
Infections such as chickenpox, shingles, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), herpes, simplex, syphilis, Lyme disease, Epstein-Barr virus and hepatitis C just to mentioned a few.
→ Metabolic conditions
Diabetes mellitus and elevated uric acid can cause Diabetic peripheral neuropathy and it requires special attention as it’s by far the most common cause of peripheral neuropathy. It is estimated that around 60% of diabetic patients suffer from a form of peripheral neuropathy, been PN the number one cause of non-traumatic lower extremity amputations in US.
→ Vascular conditions
Ones such as heart failure – in which the heart is unable to pump properly – this causes a decrease in blood flow and oxygenation to the peripheral nerves causing inflammation and damage. Other vascular condition known as Peripheral artery disease may also cause neuropathic pain. Peripheral artery disease is a narrowing of the arteries commonly found in the lower extremities – thighs, hips, buttocks, legs and calves – chronic narrowing of these arteries causes a decrease in blood flow, decrease oxygenation and nerve damage over time.
The American Autoimmune Related Diseases Association (AARDA) estimates that about 20 million Americans have one or more forms of peripheral neuropathy.
→ Other metabolic conditions
Liver and kidney disease could lead to nerve damage due to the exposure of waste products the liver and the kidneys are unable to remove.
→ Toxins/Heavy Metals
Exposure to these agents could lead to nerve inflammation and damage over time. Some examples include lead, mercury, arsenic and organic solvents among others.
→ Chronic Alcohol Intake
Alcohol can be toxic to the nerves just by itself if you drink in large quantities. In addition, chronic alcohol intake interferes with the absorption of important nutrients for the function of healthy nerves.
Thiamine, folate, niacin, vitamins B6 and B12, are all needed for proper nerve function, drinking too much can alter levels of these nutrients; fortunately, by cutting out the intake, improving the diet and supplementing with certain vitamins, it can be reversed.
→ Autoimmune Conditions
Autoimmune diseases occur when your immune system that normally defend us from viruses, bacteria mistakenly attack and destroys healthy tissue in your body. Some of these diseases, such as multiple sclerosis and Gillian-Barre, attack nerve tissue directly.
Some autoimmune conditions associated with peripheral neuropathy include Lupus, Rheumatoid arthritis, Psoriasis, Guillain-Barre syndrome, Sjogren’s syndrome just to mention a few.
It is estimated that 30-40% of patients with cancer have a form of peripheral neuropathy.
→ Chemotherapy drugs
It is estimated that 30-40% of patients with cancer have a form of PN. Nerve cells (neurons) are one of the most sensitive cells to chemotherapy. Some drugs may cause symptoms immediately after treatment has finished but others may have delayed onset presenting months or even years after the last treatment was give.
Other drugs apart from chemotherapy agents that may also cause neuropathy include anti-seizure medications, HIV meds, some antiparasitic agents and blood pressure drugs as well. Some examples include anti-seizure medications such as carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbital. Heart or blood pressure medications such as Amiodarone or Hydralazine. Drugs that fight infection such as Nitrofurantoin, Metronidazole, Isoniazid, Hydroxychloroquine, HIV drugs, etc.